Chinese Herbal Medicine
|
Chinese herbal medicine is one modality within the broad scope of traditional Chinese medicine, which also includes acupuncture, massage (tuina), breathing exercises (qi gong), tàijí quán and dietary therapy. In the great majority of cases practitioners of Chinese herbal medicine are also qualified in acupuncture and moxibustion (burning of dried mugwort on particular points on the body) and work with both modalities as well as often with massage, dietary therapy or breathing exercises.
Good health is seen as a state in which a person has optimum energy or vitality (qi) and in which the functions needed to maintain that vitality are unimpeded. Ill-health is due to a loss of vitality or to some form of impediment to those functions, or both. Good health furthermore requires the maintenance of a dynamic equilibrium, between the two universal forces of yin and yang which requires a balance between (yin) nourishment and (yang) activity. When these become unbalanced, illness may result. |

Diagnosis requires the identification of a pattern of disharmony displayed by an individual patient, based on observation, listening, questioning and palpating.
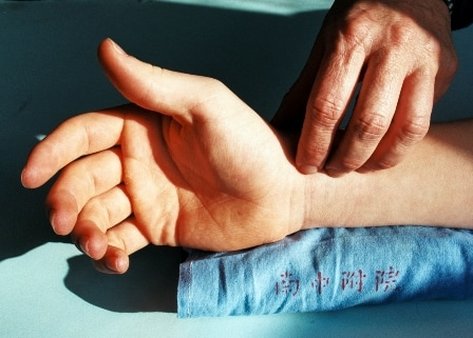
Particular attention is paid to the tongue and pulse in evaluating the patient’s condition. A disharmony may be read as a deficiency or dysfunction in one or more of the vital internal organs which refer to spheres of function, and should not to be confused with the anatomical organs of modern medicine. Another perspective in diagnosis involves identifying patterns according to the presence of pathogenic factors. Such factors, which are not to be thought of as just microbes, are described in terms derived from the natural world, namely heat, cold, dampness, wind, dryness, together with varieties of toxin and disease-causing products of the body described as blood stasis and phlegm. These patterns may have an external origin in climate or environment. For example, a damp house or damp working conditions may lead to a damp condition affecting the joints; a hot environment may aggravate a hot condition affecting the skin.
The Chinese materia medica contains several hundreds of plant species, together with some non-plant ingredients (not used in the UK). These are classified according to their ‘temperature’, flavour, direction of movement, and properties that are related to their ability to supplement or clear impediments to function. The art of treatment with Chinese herbal medicine is to choose a formula (a combination of herbs) which matches the pattern of disharmony of the individual, and to modify the formula to accommodate changes in the course of treatment.
Particular attention is paid to the tongue and pulse in evaluating the patient’s condition. A disharmony may be read as a deficiency or dysfunction in one or more of the vital internal organs which refer to spheres of function, and should not to be confused with the anatomical organs of modern medicine. Another perspective in diagnosis involves identifying patterns according to the presence of pathogenic factors. Such factors, which are not to be thought of as just microbes, are described in terms derived from the natural world, namely heat, cold, dampness, wind, dryness, together with varieties of toxin and disease-causing products of the body described as blood stasis and phlegm. These patterns may have an external origin in climate or environment. For example, a damp house or damp working conditions may lead to a damp condition affecting the joints; a hot environment may aggravate a hot condition affecting the skin.
The Chinese materia medica contains several hundreds of plant species, together with some non-plant ingredients (not used in the UK). These are classified according to their ‘temperature’, flavour, direction of movement, and properties that are related to their ability to supplement or clear impediments to function. The art of treatment with Chinese herbal medicine is to choose a formula (a combination of herbs) which matches the pattern of disharmony of the individual, and to modify the formula to accommodate changes in the course of treatment.
Contact us: [email protected]